Table of contents
This document explains the requirements and the design of support utilities for persistence.
Introduction
Even though Hibernate when used with Spring is a complete persistence framework, we need
some utilities and support classes to make Hibernate easier to use.
Requirements
- The persistence framework shall make it easy to implement new persistent classes
for Hibernate with a primary key and version.
The package can be extended inthe future with for instance:
- Useful generic persistent classes such as key-value pairs, binary arrays, and persisting
documents as XML.
Design
The persistence framework provides the following:
- A interface and abstract class for making it easy to implement persistent objects.
- A base class to for implementation of Hibernate DAOs.
Structure
Package Overview
Persistence support is provided in two packages:
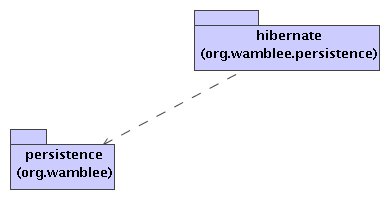
Package org.wamblee.persistence provides interface and utility classes for
persistence.
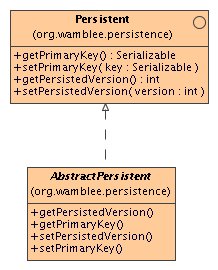
Support for persistent objects
The Persistent interface is the interface that every persistent object must
implement. It provides methods for getting and setting primary key and version. These
methods should only be used by DAO implementations and never (!) by application code.
Specifically, equals() and hashCode() should also not use these
methods.
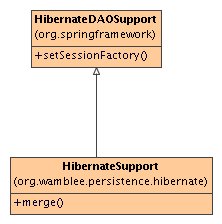
Support for DAOs
The HibernateSupport class extends the Spring
HibernateDAOSupport class with useful methods for DAOs.
The following methods are provided:
- merge(): This extends the standard Hibernate merge()
operation by also setting the primary keys and versions of the object passed into the
merge operation. Standard Hibernate does not do this. Care should be taken with this
operation since it will lazy load all associations of the object passed to the merge
operation if merge was specified for the cascade attribute in the
Hibernate mapping file
Dynamics
Since the current design is trivial, no sequence diagrams are provided.
Design Rules
To use persistence support effectively, the following rules should be followed:
- Every persistent object should implement the Persistent interface
- Application functionality should not(!) depend on the primary key or version of the
object.
- The merge() method of HibernateSupport should be used with
caution as it will lazy load all assocations mapped with cascade="merge".
- A data access object should never allow low-level database exceptions to pass through,
unless the occurence of such an exception would mean that a problem in the implementation
exists.
- It is recommended to implement data access in such a way that it does not depend on
catching and interpreting database exceptions. Doing this would tie the DAO implementation
to a database in general and to certain database features in particular. Specifically,
foreign key constraints and primary keys are nice mechanism if the database has them, but
these should only be used to prevent data corruption and guard against programming errors.
Application functionality should not depend on the support of these features in the
persistence layer.